New clinical Precision Medicine population 48-week data demonstrates unprecedented cognitive stabilization in early Alzheimer’s disease
Cognitive outcomes observed in the oral blarcamesine 30 mg Precision Medicine cohort move toward normal aging profiles across validated clinical scales, supporting its relevance in early-stage Alzheimer’s care
84.7% reduction in decline at 48 weeks of blarcamesine treatment vs placebo on the primary cognitive endpoint ADAS-Cog13
Blarcamesine could represent a novel treatment option for up to ~70% of early Alzheimer’s patients benefiting from further improved outcomes using directed Precision Medicine to alleviate significant medical and economic burden
NEW YORK – September 9, 2025
Anavex Life Sciences Corp. (“Anavex” or the “Company”) (Nasdaq: AVXL), a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on developing innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, neurodevelopmental, neurodegenerative, and rare diseases including Rett syndrome, announced today the latest findings for blarcamesine, an oral small molecule for the potential treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
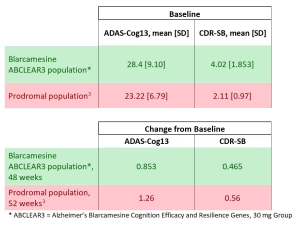
On all standard scales for measuring Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline, after 48 weeks, the defined Precision Medicine population ABCLEAR3 [1] consisting of early AD patients with confirmed and progressed pathology taking 30 mg once-daily oral blarcamesine demonstrated barely detectable decline, comparable to minimally perceptible decline in prodromal (pre-dementia) aging adults.
- For ADAS-Cog13, blarcamesine showed a 48-week change from baseline of 0.853 compared to ~1 point typical annual decline in prodromal adults.
- For CDR-SB, blarcamesine demonstrated a change from baseline of 0.465, aligning with the 0–0.5 point annual range seen in prodromal aging.
These data approximate barely detectable prodromal AD decline despite more advanced impairment at baseline within the blarcamesine population. [2], [3]
In comparison, the placebo group in the ANAVEX2-73-AD-004 Phase IIb/III ABCLEAR3 [4] population showed an ADAS-Cog13 decline of 5.592 points, resulting in a mean difference of -4.739 [95% CI -7.370, -2.108]; P=0.0004. This equals an 84.7% reduction in decline with blarcamesine treatment vs placebo.
“Given the strong interest in living a longer life without Alzheimer’s dementia, novel therapeutic directions are required. Blarcamesine’s mechanism of autophagy restoration via SIGMAR1 activation addresses a non-amyloid, upstream target, representing such a highly transformative clinical innovation,” said Marwan Noel Sabbagh, MD. “Today’s findings show the superior effect of blarcamesine in shifting typical Alzheimer’s cognitive decline to levels resembling prodromal older cognitive aging.”
“Today’s data exemplify how precision medicine is transforming Alzheimer’s care – oral blarcamesine enables a shift from fit-for-all approaches to individualized, tailored therapy,” commented Audrey Gabelle, MD, PhD. “Ensuring equitable access to effective Alzheimer’s treatments is a societal responsibility. Blarcamesine offers a safe, scalable, patient-friendly option compatible with diverse care settings.”
The mechanistic evidence that blarcamesine restores impaired autophagy through SIGMAR1 activation was previously established in vitro and in vivo, demonstrating enhanced autophagic flux, increased proteostasis capacity, and amelioration of protein-aggregation-induced paralysis in C. elegans. [5],[6]
A Precision Medicine approach confirmed that the SIGMAR1 non-mutated ABCLEAR1 population [7], representing up to ~70% of the global population, achieved deeper clinical responses than the ITT population, supporting SIGMAR1 activation as a key therapeutic mechanism.
“Our company’s goal is to provide potential high-quality options for patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Today’s updated Phase IIb/III efficacy data add important context showing strong protection from Alzheimer’s disease using an oral, once-daily therapeutic solution,” said Juan Carlos Lopez-Talavera, MD, PhD.
“We believe these data reinforce the opportunity to transform treatment paradigms for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease. Blarcamesine’s combination of efficacy, safety, and convenient oral administration may streamline treatment pathways and expand access to care,” added Christopher U. Missling, PhD, President and CEO.
Anavex will continue to evaluate Phase IIb/III early Alzheimer’s disease results and ATTENTION-AD trial data, which will be published and presented at international AD conferences.
This release discusses investigational uses of an agent in development and is not intended to imply efficacy or safety. There is no guarantee that investigational uses will complete clinical development or receive regulatory approval.
About Anavex Life Sciences Corp.
Anavex Life Sciences Corp. (Nasdaq: AVXL) is a publicly traded biopharmaceutical company developing novel therapeutics for neurodegenerative, neurodevelopmental, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Further information is available at www.anavex.com, and the Company can be followed on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
Forward-Looking Statements
Statements in this press release that are not historical are forward-looking statements. These are based on current expectations and involve risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ materially. See the Company’s most recent Form 10-K filed with the SEC for risk factors. Anavex undertakes no duty to update forward-looking statements.
For Further Information:
Anavex Life Sciences Corp.
Research & Business Development — Toll-free: 1-844-689-3939 — Email: info@anavex.com
Investors: Andrew J. Barwicki — Tel: 516-662-9461 — Email: andrew@barwicki.com
[1] ABCLEAR3 definition.
[2] MMSE prodromal comparison.
[3] McDougall et al., JPAD 2021.
[4] ABCLEAR3 placebo comparison.
[5] Christ et al., 2019.
[6] Baeken et al., 2025.
[7] ABCLEAR1 definition.
